Electrostatics & Hazardous Areas
03/21/2017
The whole phenomenon was looked upon as magic or Black Art.
At the same time the natural phenomenon of Lightning was being considered as more mysterious,beyond human comprehension, well hidden & owned by the gods.
Electrostatic & Explosive Atmosphere

Why Electrostatics ?

But now Electrostatics is an everyday phenomenon due to the development & extensive use of POLYMERS & other man-made materials in such common-use items as
FLOORING , FURNISHINGS , CLOTHING & many ENGINEERING Materials.
This everyday phenomenon is now a SAFETY Concern because of the ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE.
Electrostatics is associated with following parameters :
- Quantity of charge
- Capacitance
- Potential Difference
The following simple electrical circuit can help us to understand the relations between involved parameters .
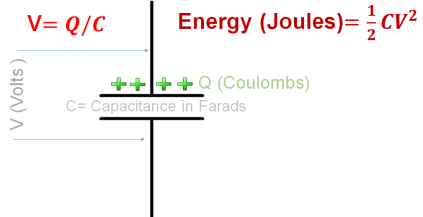
The Potential Difference across a capacitor with capacitance C and accumulated charge Q is V= Q ⁄ C
V = The potential difference across the capacitor in VOLTS
Q = The total quantity of charge on the capacitor in COULOMBS
C = The capacitance of the capacitor in FARAD
Generation of Static Electricity
First, let us get familiar with the following technical terms: – (IEC TR 61340-1)
TRIBOELECTRIC Charging
“Electrical Charging process in which charge is generated by the contact & separation of TWO surfaces which may be SOLD, LIQUID or PARTICLE-CARRYING Gases.”
A very simple process indeed, for generating electrical Charges.
Nearly all of our industrial process have this simple but important process inherently built in.
Obviously TRIBOCHARGE Generators ARE VERY COMMON AND exist all around us.
The most interesting example of TRIBOCHARGE GENERATOR is MAN
(yes! You & me)
My casual walk across a carpeted room can generate enough static charge, which upon DISCHARGE can ignite an explosive mixture.
That is why Static is off-limits to Hazardous Areas & we have IEC 60079-32-1
This simple & common process of physical contact & separation of different materials is deeply embedded in our daily routines and the resulting effect, whether we sense it or not, is also a part of our daily lives.It is true to some extent that we humans always carry charges on our bodies.
Electrostatic Charge GENERATION ( IEC TR 61340-1, 2012)
Electrostatic Charging can occur due to the following :
- CONTACT & RUBBING
- CHARGE TRANSFER
- INDUCTION (IN AN ELECTRIC FIELD)
- DUE TO POLARIZATION
- PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
- PYROELECTRIC EFFECT
- PIEZOELECTRIC EFFECT
- IONIZATION
- ELECTROCHEMEICAL PROCESS
Fortunately, the whole phenomenon exists & occur , naturally, in following 2 parts.
First part: Generation & Storage of Electrostatic Charges
(A common everyday Example )
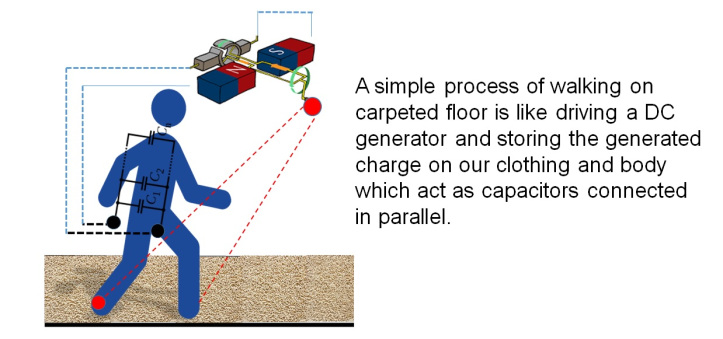
…and at the end of the walk !

Second part: Discharge (sudden or Gradual ) of this stored charges .
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
“TRANSFER OF CHARGE BY DIRECT CONTACT OR BY BREAKDOWN FROM A MATERIAL OR OBJECT AT A DIFFERENT ELECTRICAL POTENTIAL TO ITS IMMEDIATE SURROUNDINGS” ( IEC Technical Report 61340-1 2012)
An Electrostatic Discharge occurs when the strength of the electric field exceeds the dielectric thrush-hold of the atmospheric air (30kV/cm ) at normal ambient conditions.The ESD can occur in the following ways (TYPES ):
- SPARK DISCHARGE
- CORONA DISCHARGE
- BRUSH DISCHARGE
- Propagating BRUSH DISCHARGE
- CONE DISCHARGE
All these types of discharges can lead to ELECTROSTATIC IGNITION.
Now let us analyze the energy associated or contained in an ESD by recalling the basic , following, equations:
- V= Q / C Volts
- W(Energy) = 1/2 C V² (Joules)
- V= I x R
and applying on the following example.
An ungrounded metallic drum filled with powder from a grinding unit will have a charging current of (say) 100 nano-amps .Since the drum is not grounded , the resistance to ground will be very high,around, 100 GΩ.
The capacitance (by experiments ) of such a drum is about 50 pF.
The Voltage at the drum after a while will be 100 nA x 100 G = 10 kV
The maximum energy available for a possible discharge = 2.5 m J
NOW just have a look at the MINIMUM IGNITION ENERGIES of some of the Flammable liquids & gases. These materials are major players of the Hazardous Areas of our industry.
BENZENE : 0.2 mJ
Toluene : 0.24 mJ
Acetone : 1.15 mJ
(Powder ) Aluminum : 50 mJ
Obviously this DRUM can cause explosion in a Hazardous Area .
Problems caused by the ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)
Electrostatic Discharge can generate a plethora of problems including:
- Latent Defects
- Software Malfunction
- Insulation Failure
Exclusively, all electronic systems in use are vulnerable to electrostatic discharges. Any direct hit is obviously damaging due to high resulting currents and so is the indirect hit due to electromagnetic effects and induced current.
Solutions to problems of ESD in hazardous Areas
(Reference : IEC Technical Report 60079-32-1 & Technical Report TR 61340-1)
The underlying object is keep the accumulated charge, generated by electrostatic phenomenon at a minimum. This is logically achieved by :-
- Minimizing the use of INSULATING Materials . Using inherently conductive materials is one option the other option is to use insulating materials with GRADES . The properties of GRADED insulating materials lie between that of CONDUCTIVE & DISSIPATIVE material so that a proper & secure EARTH/GROUND connection can easily drain the accumulated charge .
An Example from Ex Industry
The data sheet of a Ex Certified GFRP enclosure, showing the value of surface Resistance
The resistance of DISSIPATIVE Material
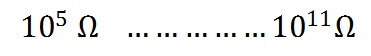
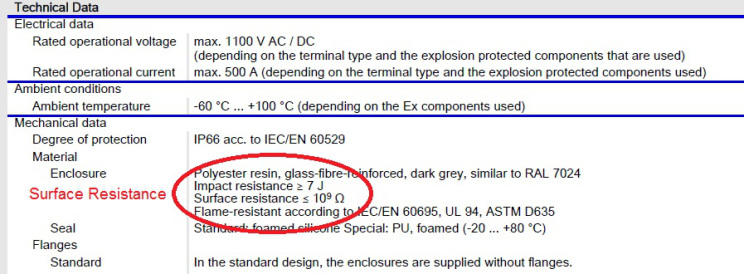
This enclosure will not add to the electrostatic charge accumulation .
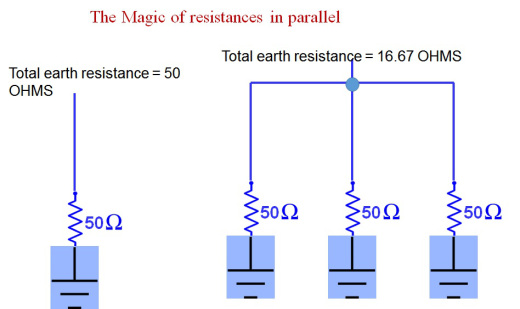
- Grounding or Earthing. The most effective method of avoiding hazard due to static electricity is to connect all conductors to earth to prevent accumulation of charges .
Grounding /Earthing & BONDING
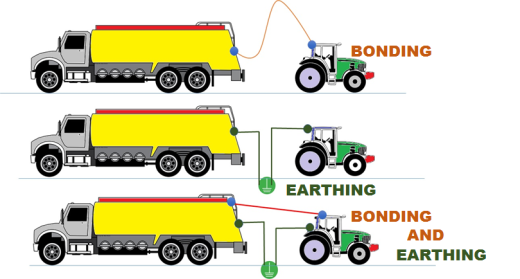
Bonding is used to minimize the Potential Difference between conductive objects to an equal value so that all conductive objects are at same Potential .The objects are not earthed.
Earthing on the other hand is a process to equalize the Potential Difference between the conductive objects and the earth.
Combination of BONDING & EARTHING is employed to maintain the potential of the system under consideration at Zero Ground Potential.
Reap the safe fruits of a good ground.
Original article:https://expeltec.com/2016/09/25/electrostatics-hazardous-areas/ https://expeltec.com/9-1-electrostatic-ex/